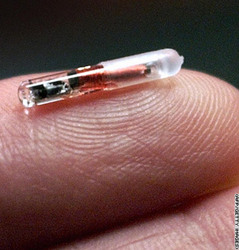
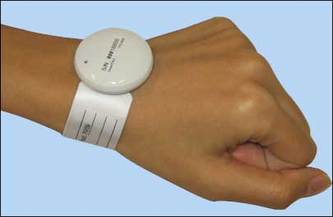
Storage Devices and RFID Applications in Healthcare
Basic Component
1) Interrogator
Depending on the application and technology used, some interrogators not only read, but also remotely write to the tags. For the majority of low cost tags, which are those tags without batteries, the power to activate the tag microchip is supplied by the reader through the tag antenna when the tag is in the interrogation zone of the reader.
2) Tag
Chip tags consist of a microchip and a coupling element,which is an antenna. Most tags are only activated when they are within the interrogation zone of the interrogator. When tags are outside the zone, they are so called "asleep". Chip tags can be both read-only, which are programmed during manufacture, or, at higher complexity and cost, read-write, or both. The size of the tag depends on the size of the antenna, which increases with range of tag and decreases with frequency. Chip tags contain memory.
3) Middleware
Middleware is the interface needed between the interrogator and the existing company databases and information management software.
Depending on the application and technology used, some interrogators not only read, but also remotely write to the tags. For the majority of low cost tags, which are those tags without batteries, the power to activate the tag microchip is supplied by the reader through the tag antenna when the tag is in the interrogation zone of the reader.
2) Tag
Chip tags consist of a microchip and a coupling element,which is an antenna. Most tags are only activated when they are within the interrogation zone of the interrogator. When tags are outside the zone, they are so called "asleep". Chip tags can be both read-only, which are programmed during manufacture, or, at higher complexity and cost, read-write, or both. The size of the tag depends on the size of the antenna, which increases with range of tag and decreases with frequency. Chip tags contain memory.
3) Middleware
Middleware is the interface needed between the interrogator and the existing company databases and information management software.
The picture above shows (from top left) : active RFID, passive RFID, microchip, RFID interrogator, Smart Tag.
Active vs. Passive RFID
Active tags refer to RFID tags which have their own power source, so they can recieve a weaker signal from the interrogator, which means it can detect the interrogator at a farther distance than passive tags. The power source on the tag boosts the return signal. These types can have ranges of hundreds of meters, but cost more because of their size and sophistication. Battery life can also limit the life of the tag.
Passive tags refer to RFID tags which are powered solely by the RFID interrogator. The interrogator emits a radio-frequency, which powers the silicon chip on the tag when it is within range of the radio-frequency field. When the power to the silicon chip on the tag meets the minimum voltage threshold it require to turn on, the silcion chip can then send back information on the same radio-frequency wave. The range is usually limited to several meters.
Semi Passive tags refer to tags with a power source. The power source usually refers to a laminar, flexible, or low cost battery, which can be used for on tag sensing, for example in taking temperature. However, semi passive tags are not used to boost range.
Passive tags refer to RFID tags which are powered solely by the RFID interrogator. The interrogator emits a radio-frequency, which powers the silicon chip on the tag when it is within range of the radio-frequency field. When the power to the silicon chip on the tag meets the minimum voltage threshold it require to turn on, the silcion chip can then send back information on the same radio-frequency wave. The range is usually limited to several meters.
Semi Passive tags refer to tags with a power source. The power source usually refers to a laminar, flexible, or low cost battery, which can be used for on tag sensing, for example in taking temperature. However, semi passive tags are not used to boost range.
Main Purpose of RFID
Real Time Patient Tracking
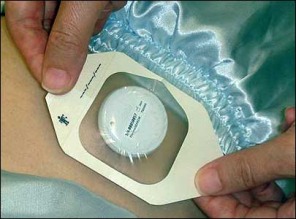
The picture on the left shows the ThermoSensors used to monitor patient's temperature.
Tan Tock Seng Hospital(TTSH) is expanding the system to include a 3-cm-wide active ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) tag taped to a patient's abdomen, to monitor that individual's body temperature and detect serious infections without waking the patient.
Extensive testing was carried out on the ThermoSensors with more than 500 patients in four hospitals. A study involving 300 patients at TTSH was also conducted at different settings, in order to compare temperature readings with various devices, such as tympanic, digital and mercury thermometers.
Results shown that the accuracy of the ThermoSensor was comparable to that of a tympanic,underarm and oral thermometer with an accuracy of within 0.2 degree Celcius.
Tan Tock Seng Hospital(TTSH) is expanding the system to include a 3-cm-wide active ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) tag taped to a patient's abdomen, to monitor that individual's body temperature and detect serious infections without waking the patient.
Extensive testing was carried out on the ThermoSensors with more than 500 patients in four hospitals. A study involving 300 patients at TTSH was also conducted at different settings, in order to compare temperature readings with various devices, such as tympanic, digital and mercury thermometers.
Results shown that the accuracy of the ThermoSensor was comparable to that of a tympanic,underarm and oral thermometer with an accuracy of within 0.2 degree Celcius.
Other Examples
When a patient is discharged, housekeeping and the bed-management unit are notified in real time, and the bed is cleaned within 30 minutes. With advance notice, the emergency department could also better prepare their patients for transfer.
Knowing the real-time location of patient also helps. When a patient goes in for an operation, ward nurses will be able to tell when an operation has been completed by virtue of the patient's location in the post-anesthesia care unit, and update the patient's family.
Knowing the real-time location of patient also helps. When a patient goes in for an operation, ward nurses will be able to tell when an operation has been completed by virtue of the patient's location in the post-anesthesia care unit, and update the patient's family.
Click here to return to the top of the page.